Publications
Please see our latest publications. Full list is available on google scholar).
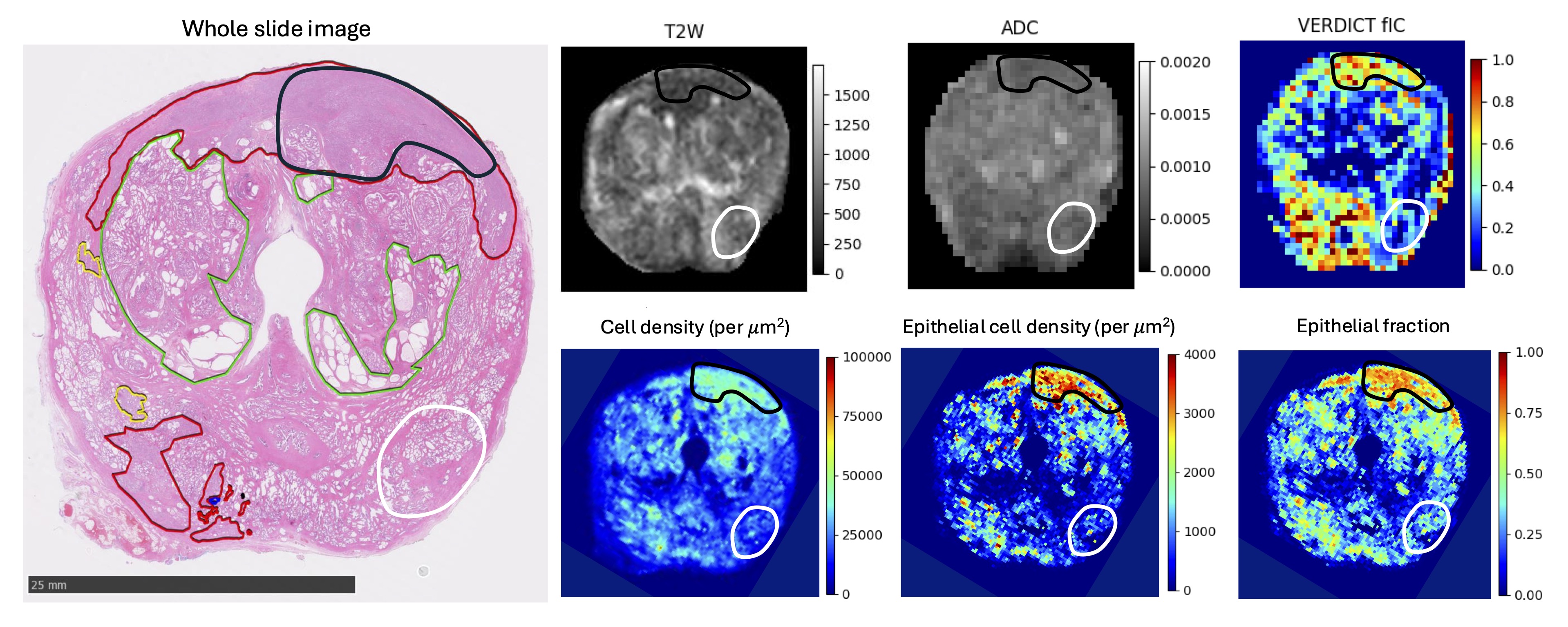
This study demonstrates strong correlations between in-vivo VERDICT fIC and histological epithelial fraction and cell density using whole-mount prostatectomy specimens, confirming fIC as a biologically grounded marker of tumour cellularity.
Marta Masramon, Manju Mathew, Saurabh Singh, Thomy Mertzanidou, Joey Clemente, Adam Retter, Natasha Thorley, Adam Phipps, Thomas Parry, Marianthi-Vasiliki Papoutsaki, Lorna Smith, Francesco Grussu, Veeru Kasivisvanathan, Alistair Grey, Eoin Dinneen, Greg Shaw, Dominic Patel, Lucy Caselton, Caroline M. Moore, David Atkinson, Aiman Haider, Alex Freeman, Daniel C. Alexander, Shonit Punwani, Eleftheria Panagiotaki
Preprint - Research Square (2025)
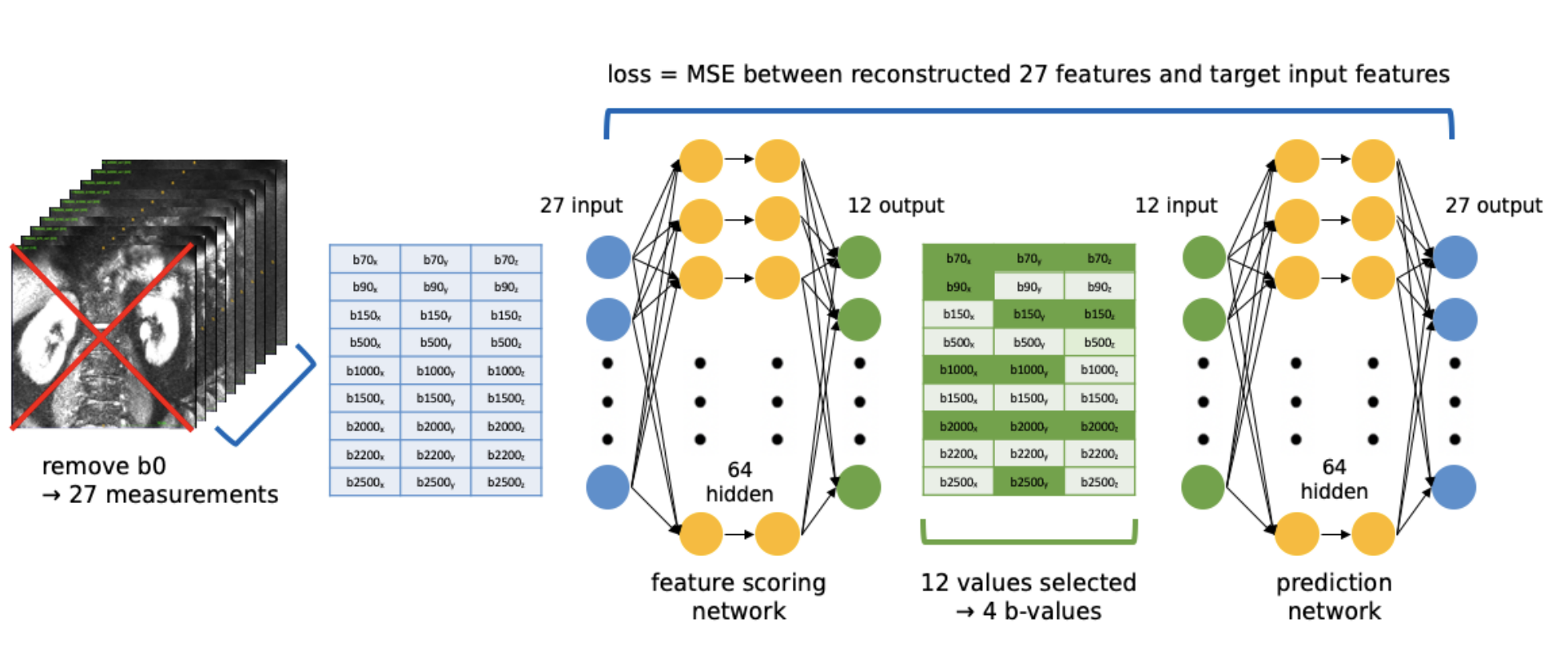
This study introduces a dual deep-learning pipeline for renal VERDICT-MRI, showing improved model fitting, significant parameter differences between tumour and normal tissue, and identifying a shortened acquisition protocol for clinical use.
Snigdha Sen, Lorna Smith, Lucy Caselton, Joey Clemente, Maxine Tran, Shonit Punwani, David Atkinson, Richard L Hesketh, Eleftheria Panagiotaki
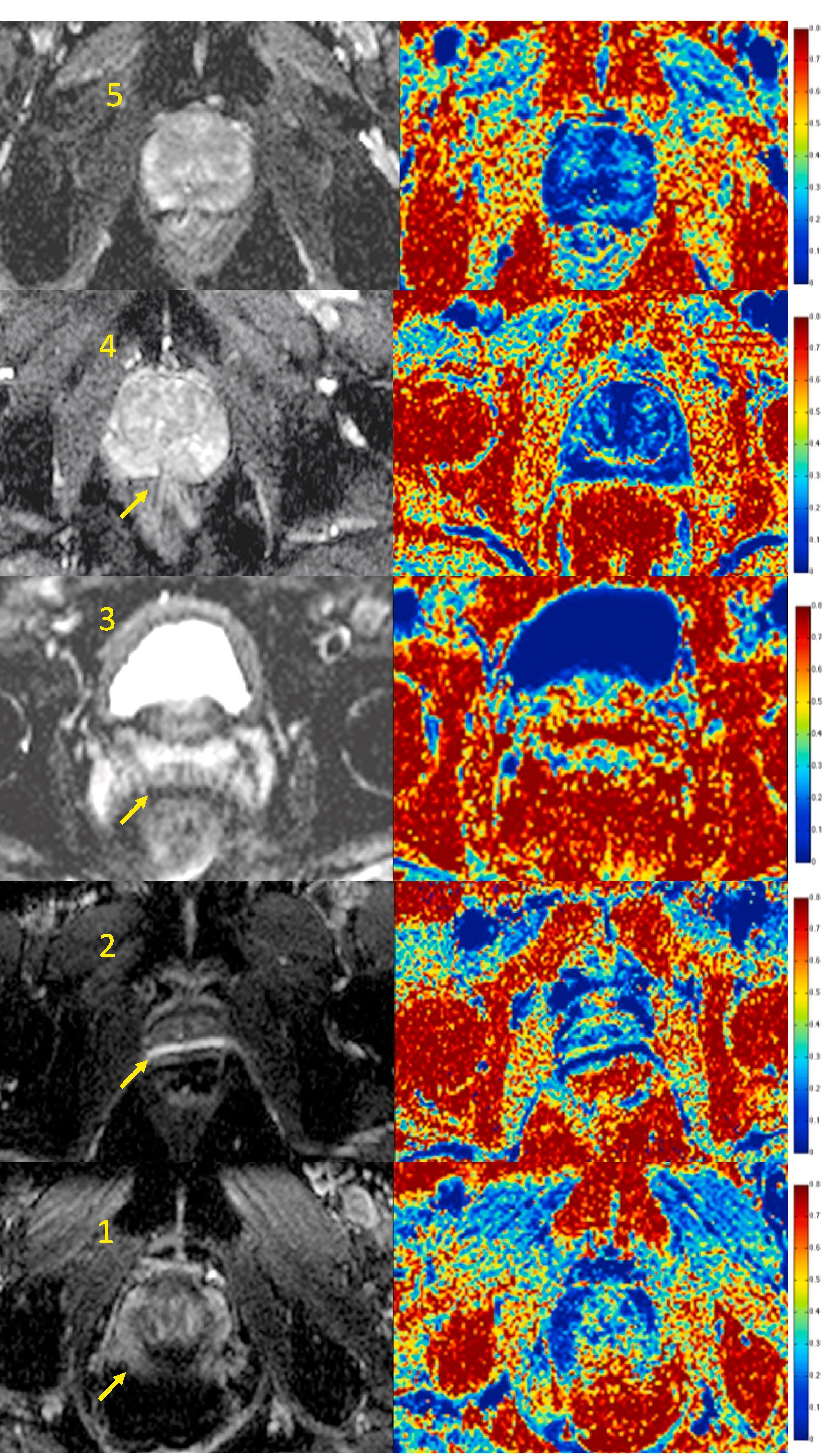
This study aimed to assess the image quality of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps derived from conventional diffusion-weighted MRI and fractional intracellular volume maps (FIC) from VERDICT MRI (Vascular, Extracellular, Restricted Diffusion for Cytometry in Tumours) in patients from the INNOVATE trial.
Saurabh Singh, Francesco Giganti, Louise Dickinson, Harriet Rogers, Baris Kanber, Joey Clemente, Hayley Pye, Susan Heavey, Urszula Stopka-Farooqui, Edward W. Johnston, Caroline M Moore, Alex Freeman, Hayley C Whitaker, Daniel C Alexander, Eleftheria Panagiotaki, Shonit Punwani
European Journal of Radiology (2023)
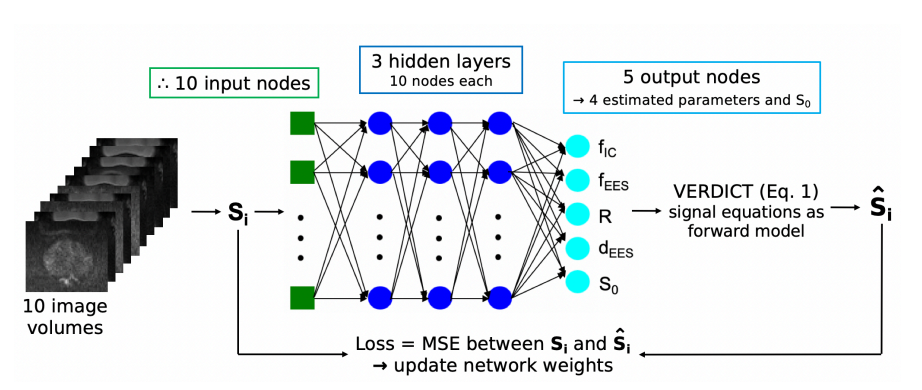
This study develops a self-supervised machine learning method to fit the VERDICT model for prostate, showing improved performance in comparison to traditional and supervised deep learning methods on both simulated and real patient data.
Snigdha Sen, Saurabh Singh, Hayley Pye, Caroline M. Moore, Hayley Whitaker, Shonit Punwani, David Atkinson, Eleftheria Panagiotaki1, and Paddy J.Slator
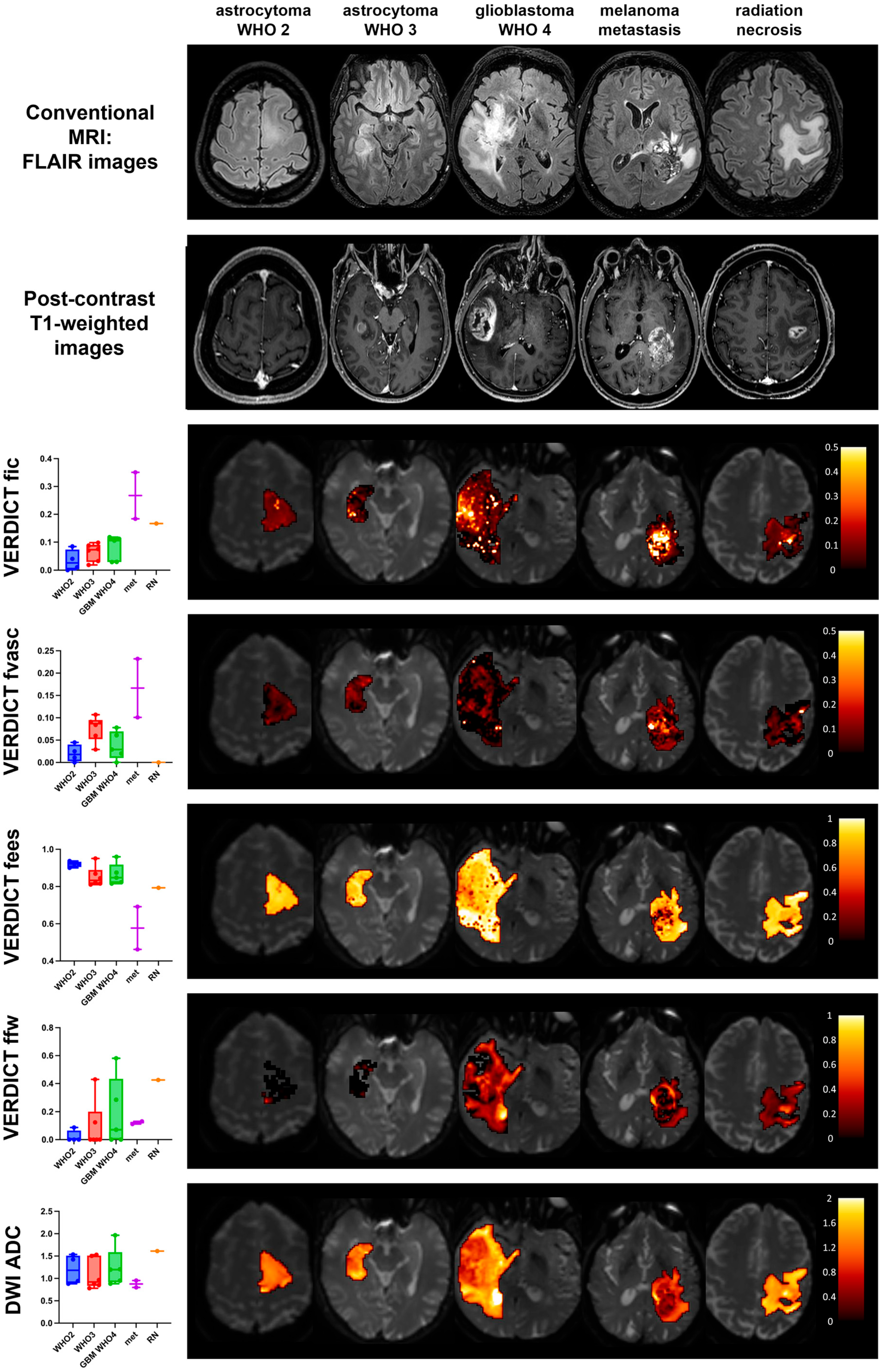
VERDICT is a diffusion MRI framework for the characterisation of different components of tumours, which has shown diagnostic utility for body cancer. This study extends the VERDICT framework to comprehensively characterise brain tumours.
Matteo Figini,Antonella Castellano,Michele Bailo,Marcella Callea, Marcello Cadioli, Marcello Cadioli, Samira Bouyagoub, Marco Palombo, Valentina Pieri, Pietro Mortini, Andrea Falini, Daniel C. Alexander, Mara Cercignani and Eleftheria Panagiotaki
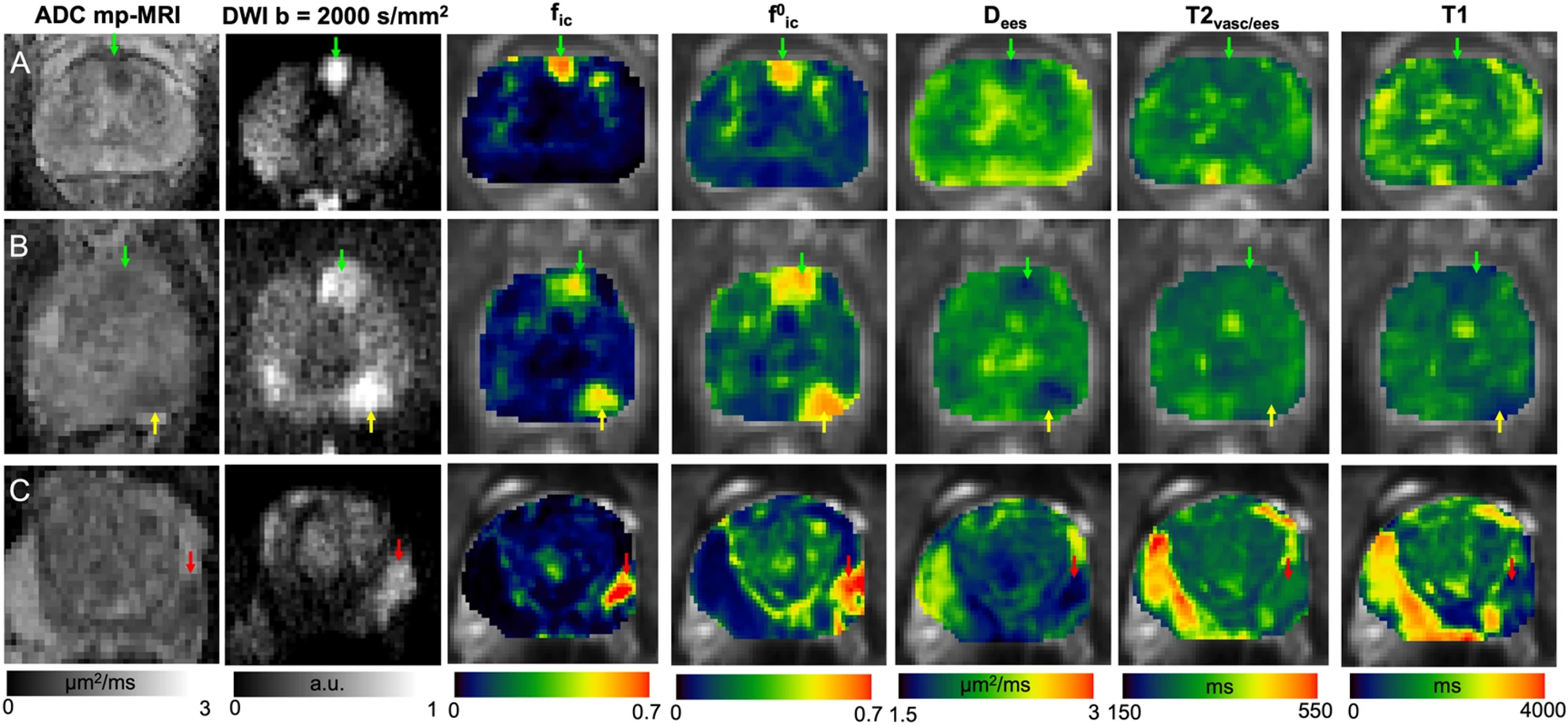
This work presents a biophysical model of diffusion and relaxation MRI for prostate called relaxation VERDICT (rVERDICT). The rVERDICT model allows for estimation of diffusion and relaxation properties of PCa sensitive enough to discriminate Gleason grades 3+3, 3+4 and larger or equal to 4+3.
Marco Palombo, Vanya Valindria, Saurabh Singh, Eleni Chiou, Francesco Giganti, Hayley Pye, Hayley C. Whitaker, David Atkinson, Shonit Punwani, Daniel C. Alexander & Eleftheria Panagiotaki
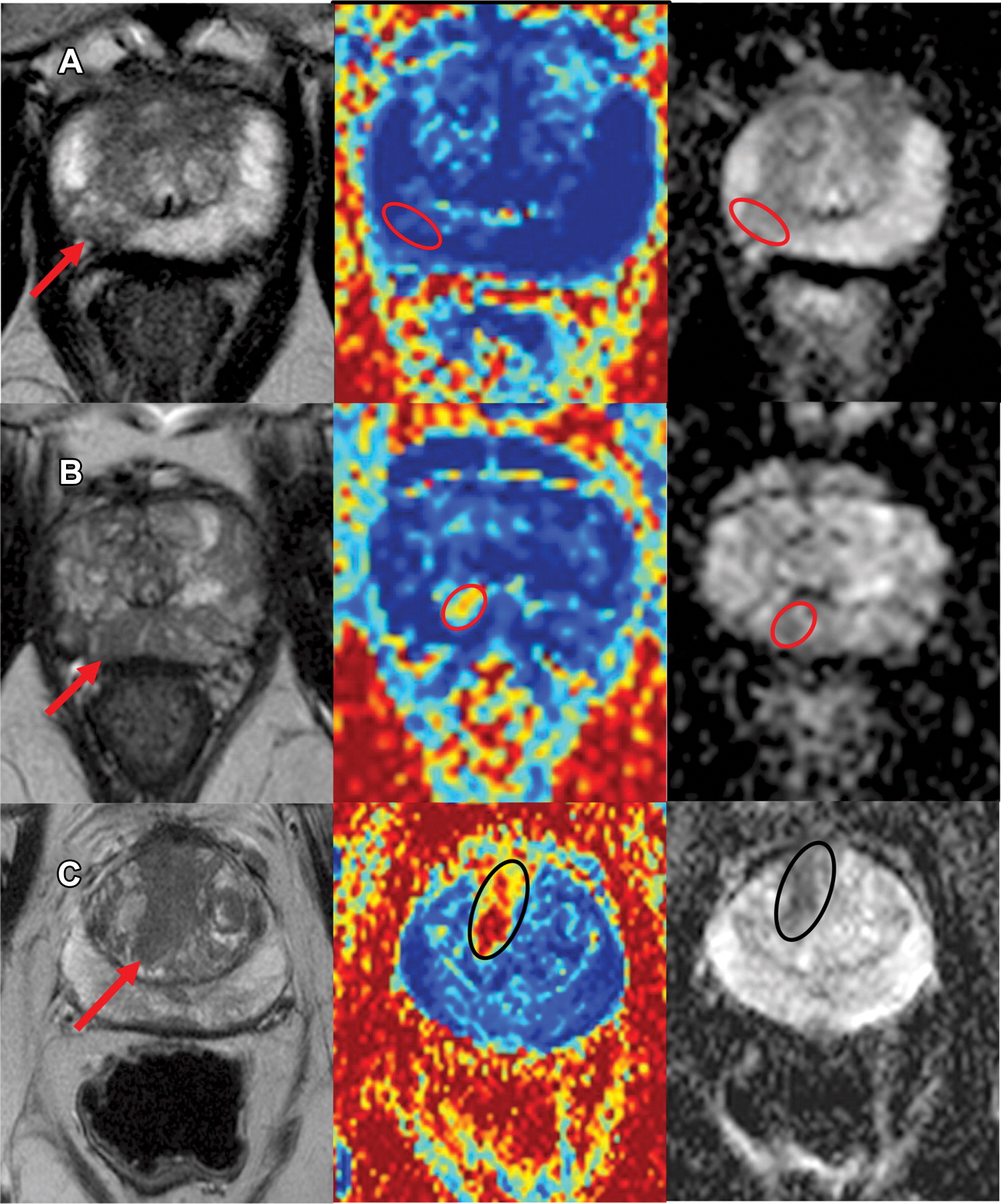
This study evaluates VERDICT MRI, mpMRI-derived apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), and prostate-specific antigen density (PSAD) as determinants of clinically significant PCa (csPCa), aiming to reduce the number of invasive procedures taking place.
Saurabh Singh , Harriet Rogers, Baris Kanber, Joey Clemente, Hayley Pye, Edward W. Johnston, Tom Parry, Alistair Grey, Eoin Dinneen, Greg Shaw, Susan Heavey, Urszula Stopka-Farooqui, Aiman Haider, Alex Freeman, Francesco Giganti, David Atkinson, Caroline M. Moore, Hayley C. Whitaker, Daniel C. Alexander, Eleftheria Panagiotaki, Shonit Punwani
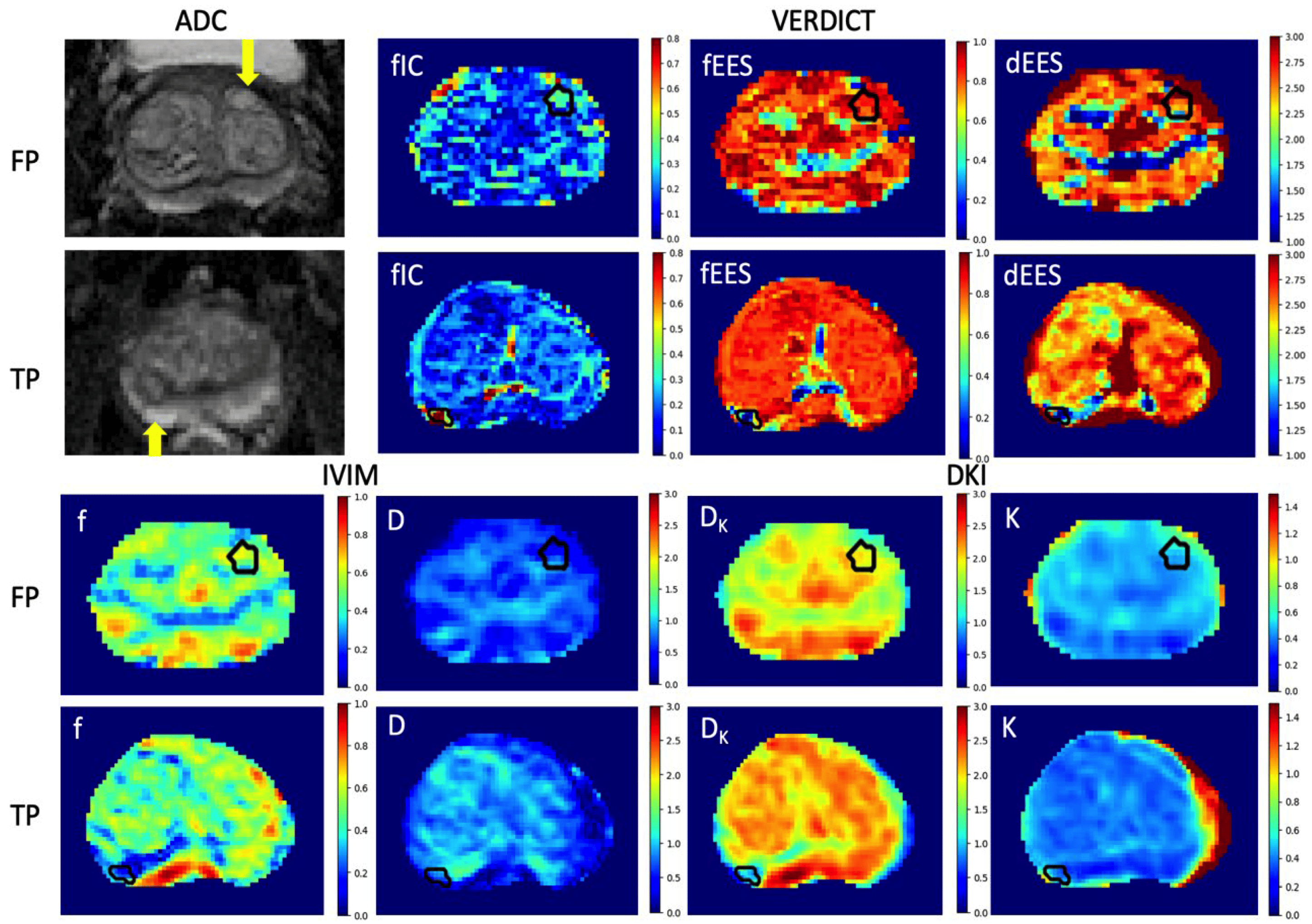
False positives on multiparametric MRIs (mp-MRIs) result in many unnecessary invasive biopsies in men with clinically insignificant diseases. This study investigated whether quantitative diffusion MRI could differentiate between false positives, true positives and normal tissue non-invasively.
Snigdha Sen, Vanya Valindria, Paddy J. Slator, Hayley Pye, Alistair Grey , Alex Freeman, Caroline Moore, ayley Whitaker, Shonit Punwani, Saurabh Singh and Eleftheria Panagiotaki
